Spring与Redis通信设计结构图
Spring与Redis通信设计结构图
Spring连接redis底层主要是采用了Redis集成组件包; spring-boot-starter-data-redis和commons-pool2,如下:
<dependency>
<groupld>ora.sprinaframework.boot</aroupld>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons </groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
</dependency>
spring-boot-starter-data-redis依赖于spring-data-redis和lettuce
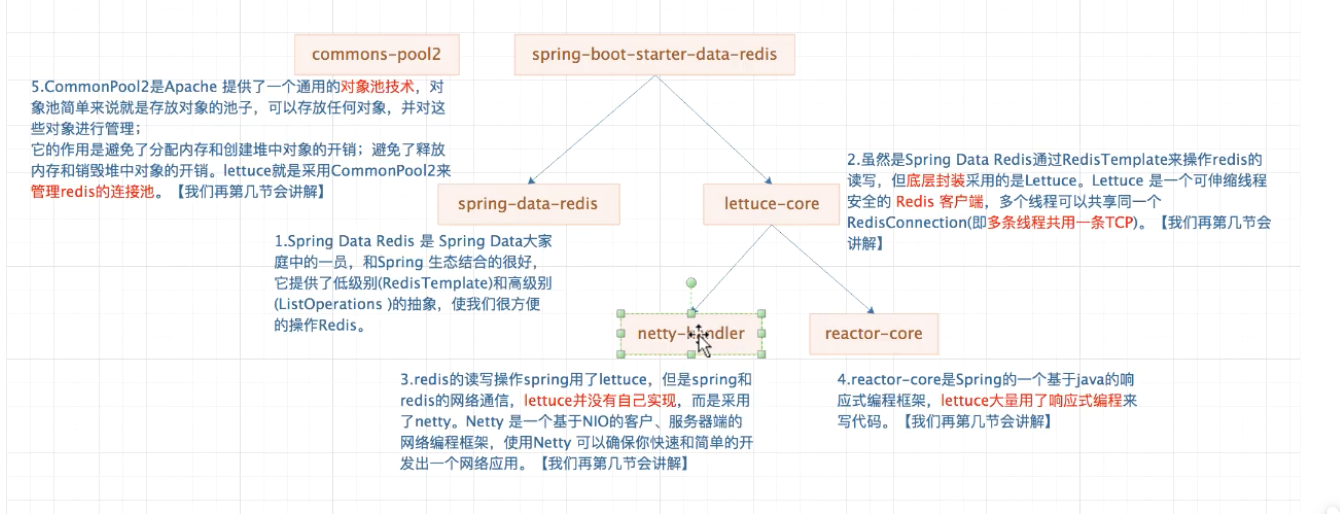
什么是lettuce

Lettuce使用的时候依赖于四个主要组件:
- RedisURI:连接信息.
- RedisClient: Redis客户端,另外集群连接有一个定制的RedisqlusterClient.
- Connection: Redis连接,主要是StatefulConnection或者StatefulRedisConnection的子类,连接的类型主要由连接的具体方式(单机、哨兵、集群)选定,比较重要。
- RedisCommands: Redis命令API接口,基本上覆盖了Redis发行版本的所有命令,提供了同步(sync)异步(async)、反应式(reative)的调用方式,对于使用者而言,会经常跟RedisCommands系列接口打交道
基于lettuce单机连接redis
@sLf4j
public class LettucecSingle {
public static void main(String[] args) {
opersingle();
}
public static void opersingle(){
//步骤1: RedisURI:连接信息
RedisURI redisUri s RedisuRI.builder()
.withHost("39.100.196.99")
.withPort (6379)
.withPassword("agan")
.withTimeout(Duration.of(10,ChronoUnit.SECONpS))
.build();
//步骤2: Redisclient: Redis客户端
Redisclient client = Redisclient.create(redisuri);
//步骤3: Connection: Redis连接 (单机)
StatefulRedisConnectionsString,string> connect = client.connect():
//步骤4: RedisCommands: Redis命令API接口
/**
* sync同步询用
*/
RedisCommands<strinq,String> commands = connect.sync();
commands, set( "hello", "hello world");
String str = commands, get("hello");
Loq. debug("---------同步-----{}-------",str);
/**
*async异步调用
*/
RedisAsyncCommandseString, String> asyncCommands = connect.async();
RedisFuturecString> future = asyicCommands.get ("helLo");
try {
String str1 = future.get();
Log.debug ("--异步--{}--",str1);
} catch (InterruptedExceptinn e){
e.printstackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
connect.close();
client. shutdown();
}
}
基于lettuce集群连 接redis
@sLf4j
public class LettucecCluster {
public static void main(String[] args) {
operCluster();
}
public static void operCluster(){
//步骤1: RedisURI:连接信息
List<RedisURL> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(RedisURL.create("redis://39.100.196.99:6381"));
list.add(RedisURL.create("redis://39.100.196.99:6382"));
list.add(RedisURL.create("redis://39.100.196.99:6383"));
list.add(RedisURL.create("redis://39.100.196.99:6384"));
list.add(RedisURL.create("redis://39.100.196.99:6385"));
list.add(RedisURL.create("redis://39.100.196.99:6386"));
//步骤2: RedisClusterClient: Redis集群客户端
Redisclient client = Redisclient.create(list);
//步骤3: Connection: Redis连接 (集群)
StatefulRedisConnectionsString,string> connect = client.connect():
//步骤4: RedisCommands: Redis命令API接口
/**
* sync同步询用
*/
RedisCommands<strinq,String> commands = connect.sync();
commands, set( "hello", "hello world");
String str = commands, get("hello");
Loq. debug("---------同步-----{}-------",str);
/**
*async异步调用
*/
RedisAsyncCommandseString, String> asyncCommands = connect.async();
RedisFuturecString> future = asyicCommands.get ("helLo");
try {
String str1 = future.get();
Log.debug ("--异步--{}--",str1);
} catch (InterruptedExceptinn e){
e.printstackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
connect.close();
client. shutdown();
}
}
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: