Reverse LinkedList
Reverse Linked List
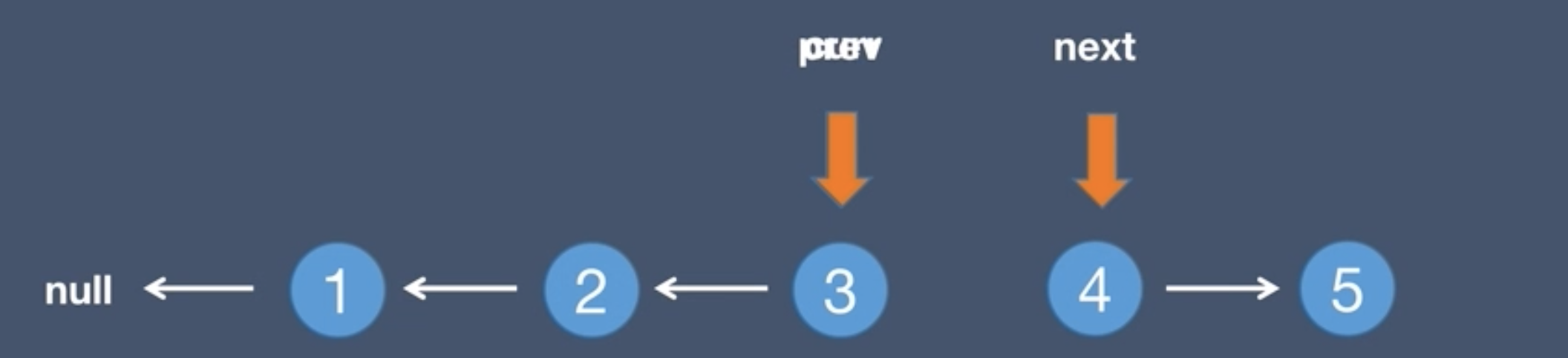
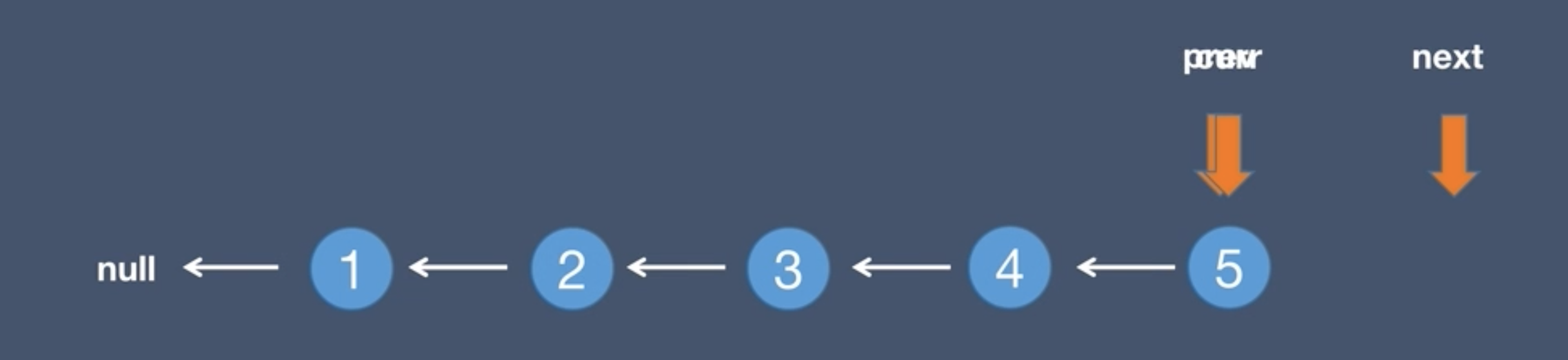
Solution (Traverse the linked list, pointing the next of each node to the previous node)
- Save the next of the current node,
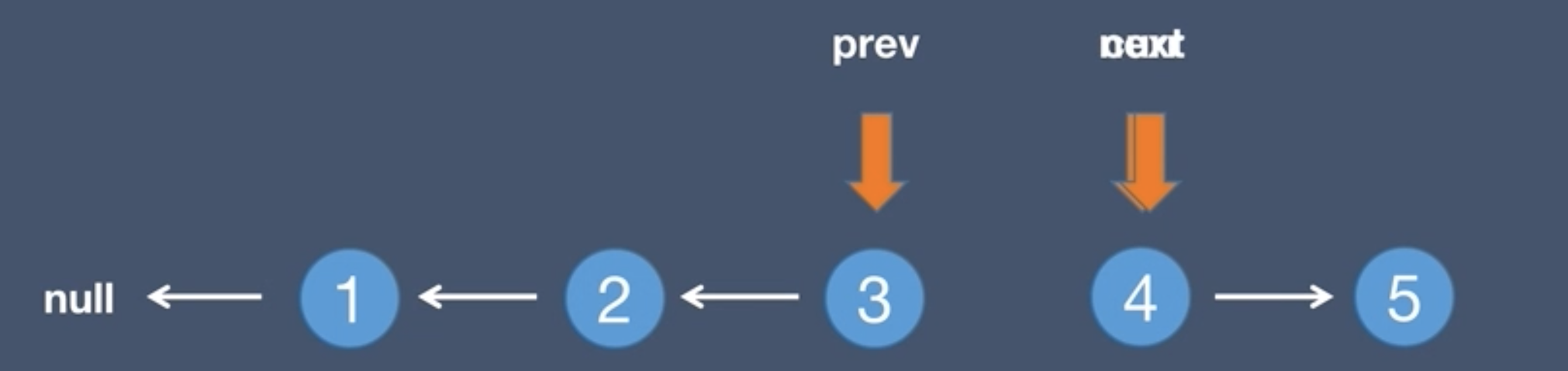
next = curr.next - Point the next of the current node to the previous node,
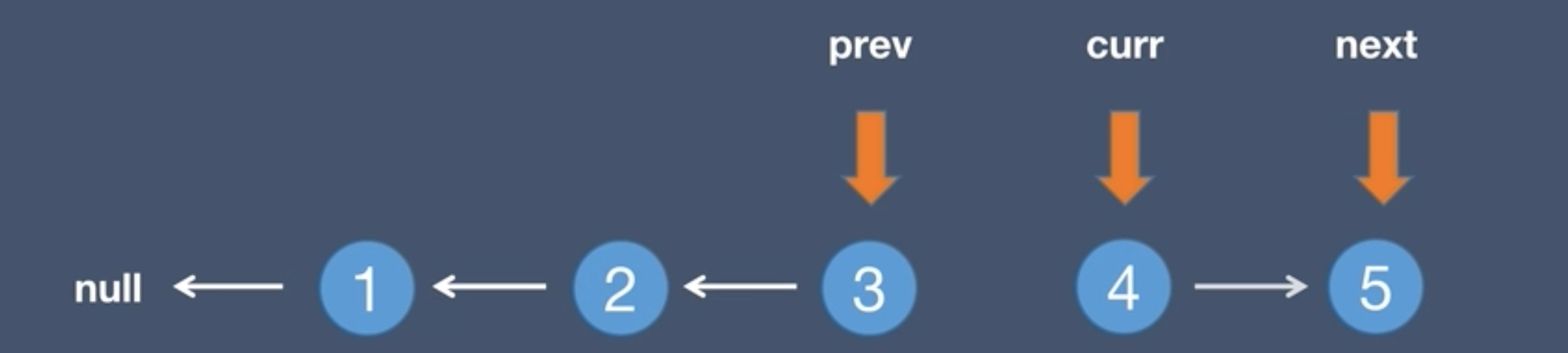
curr.next = prev - Move the forward pointer back to
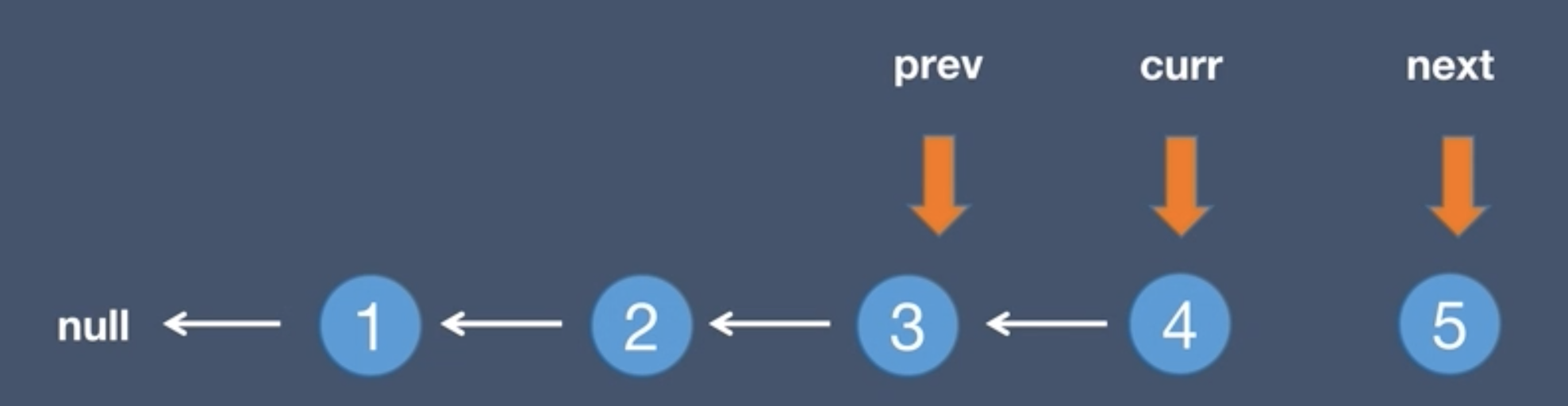
prev = curr - Move the current pointer back to
curr = next
Step
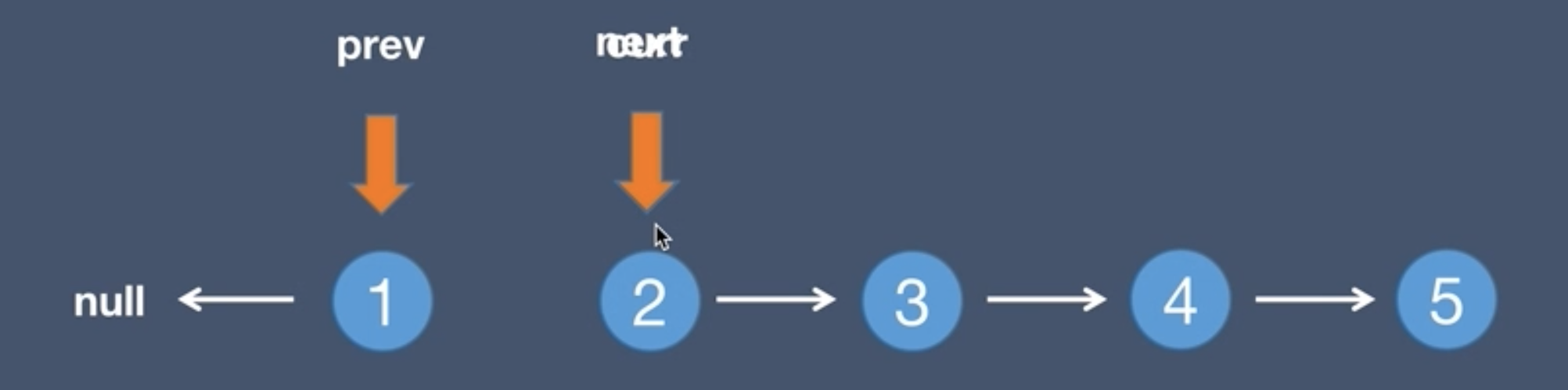
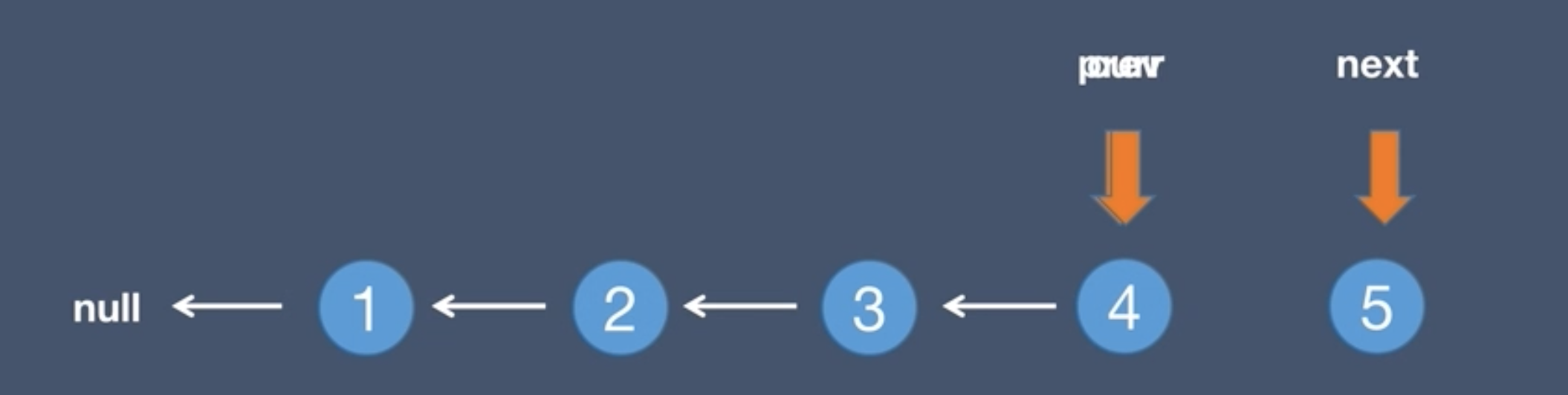
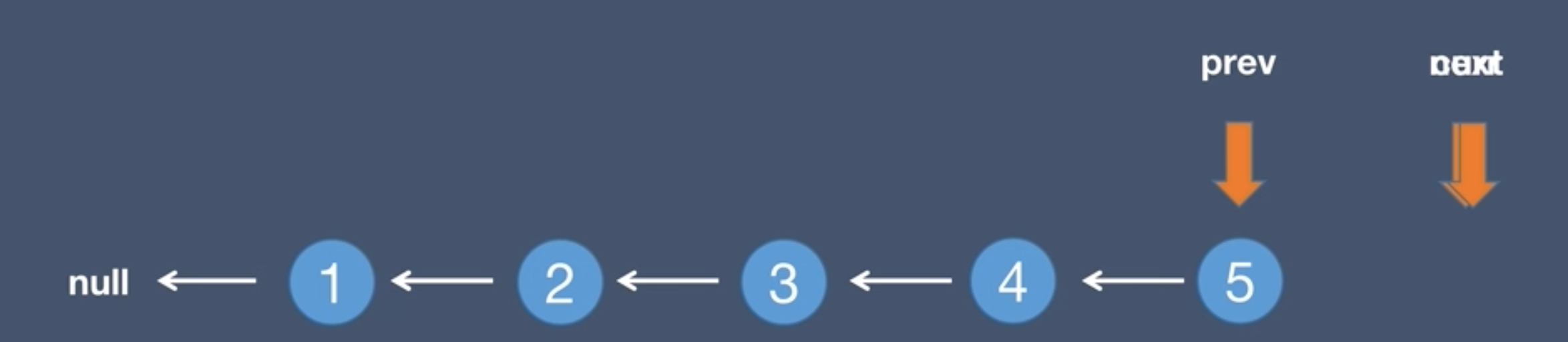
1.Initial list and pre node
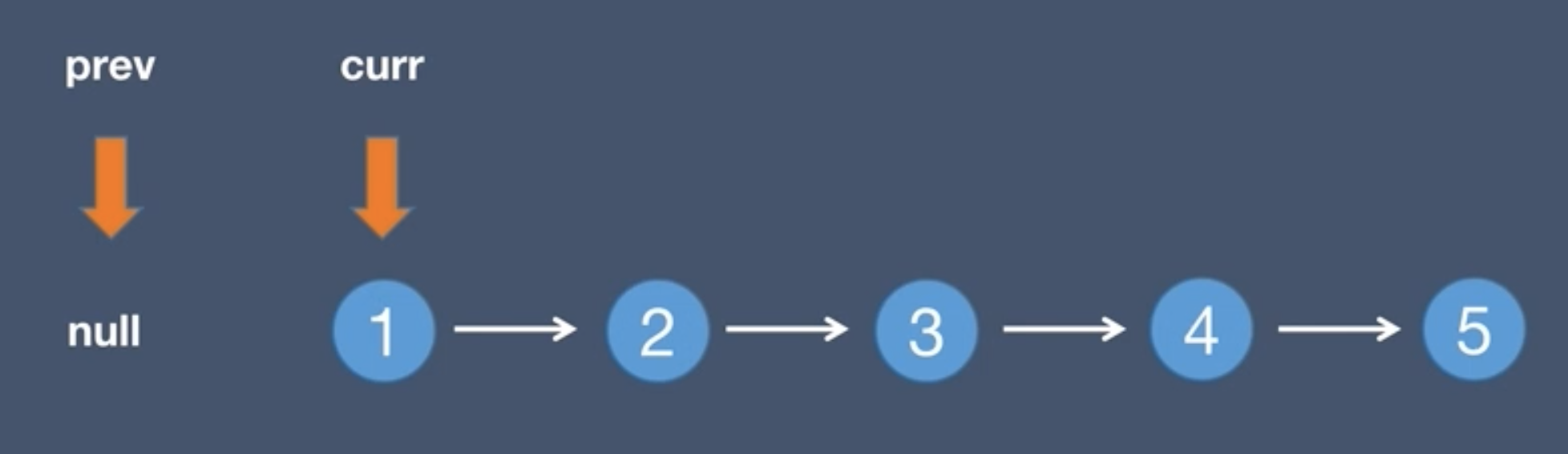
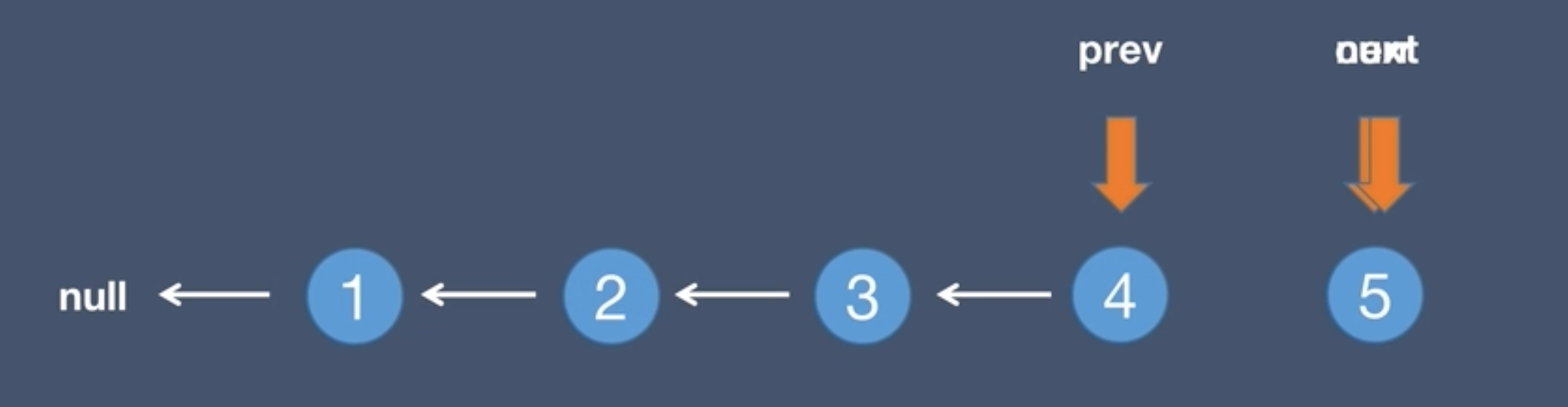
2.Initial list and next node, next = curr.next
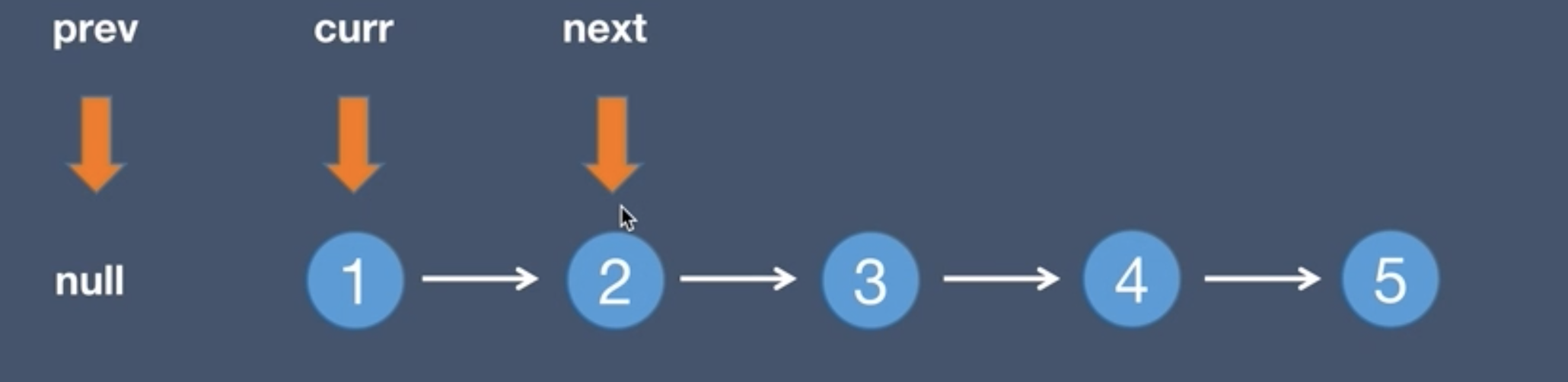
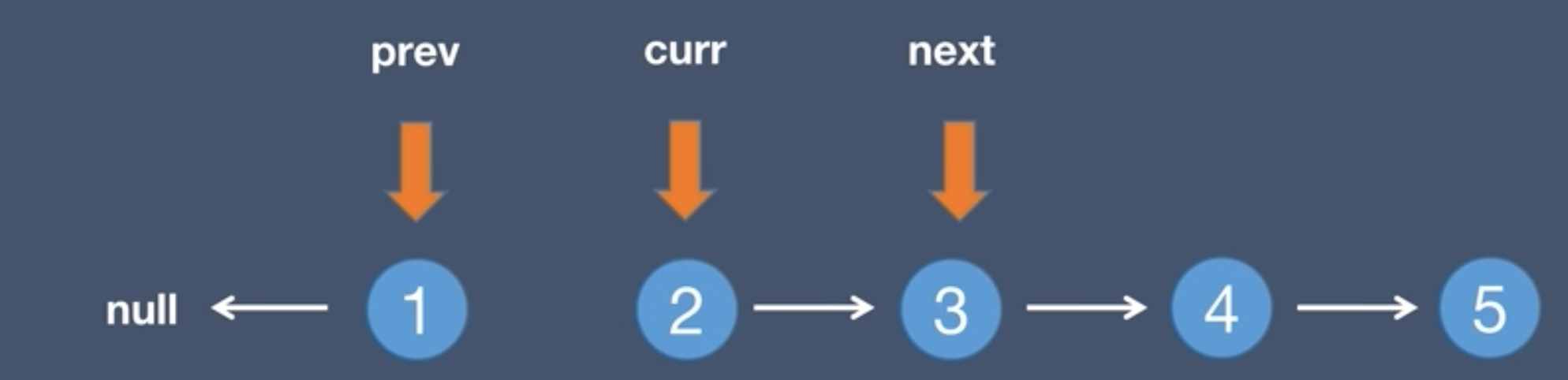
3.The current.next points to the pre node, curr.next = prev
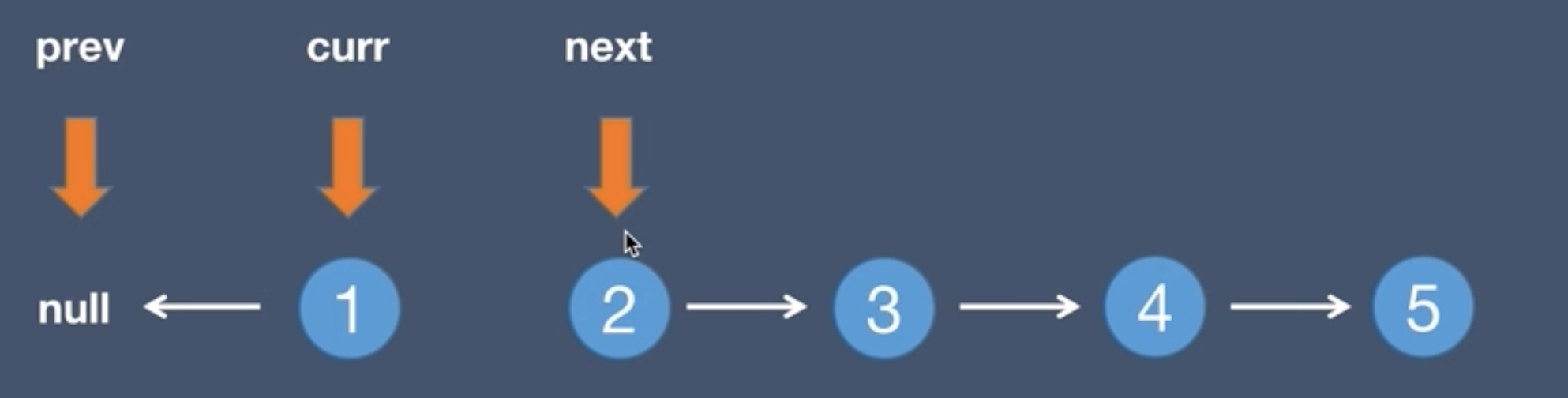
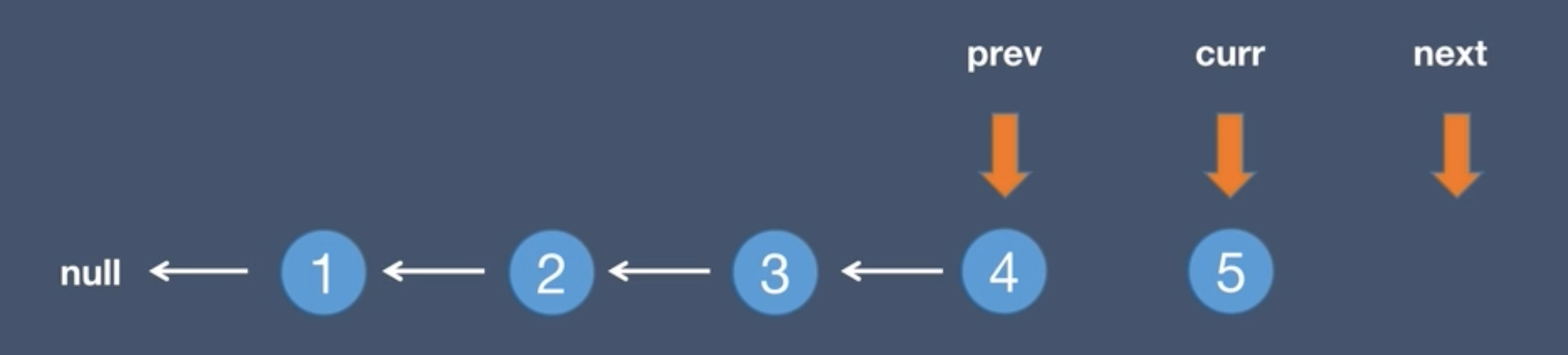
4.The pre node points to the current node, prev = curr
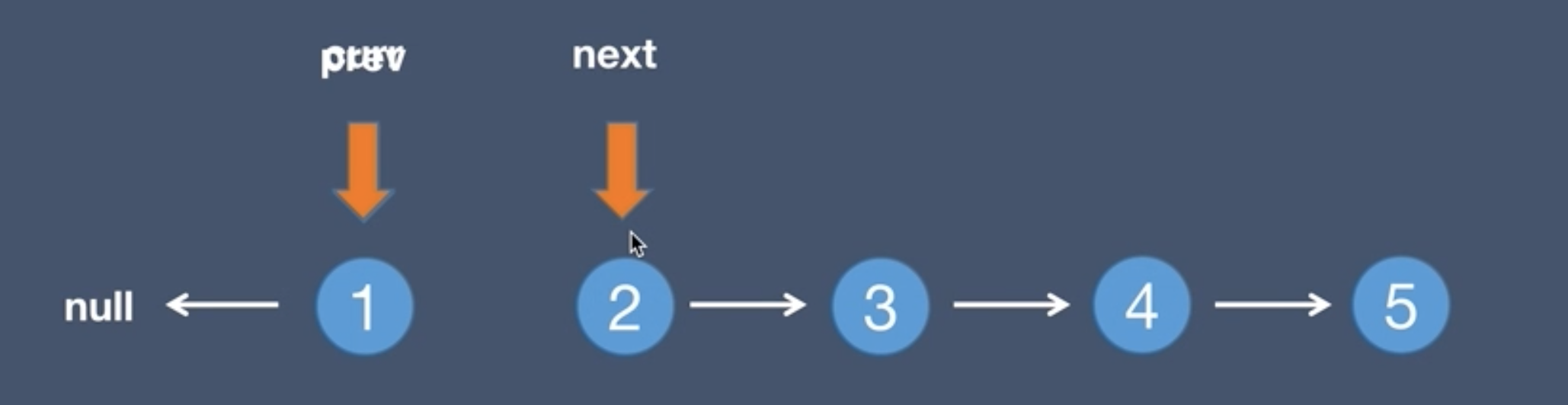
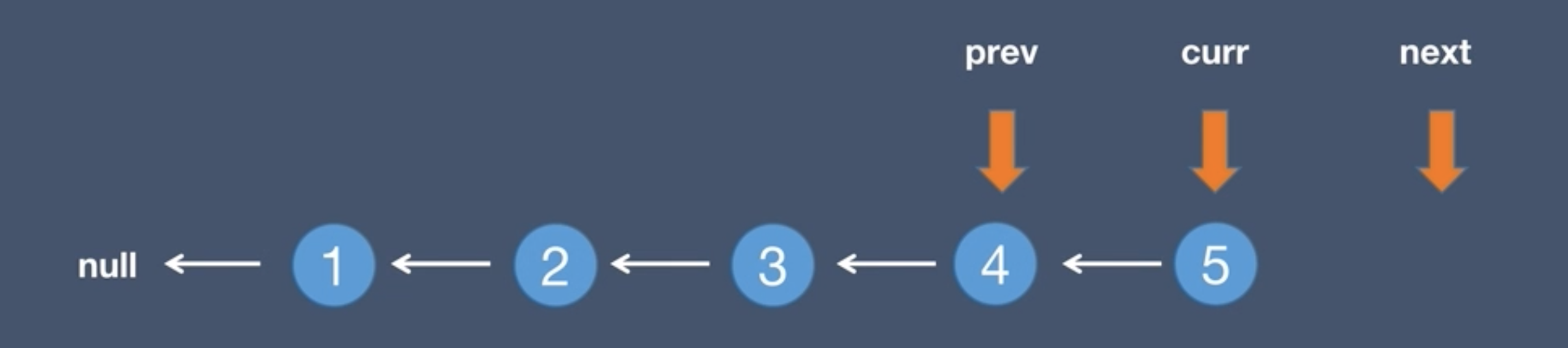
5.The current node points to the next node, curr = next
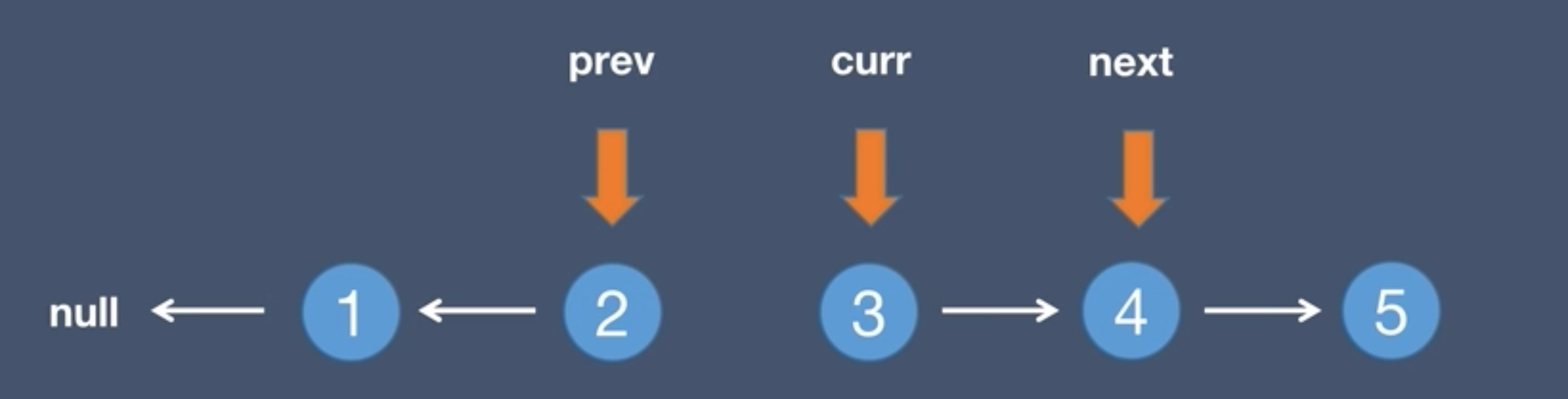
6.The next node moves to the current.next, next = curr.next
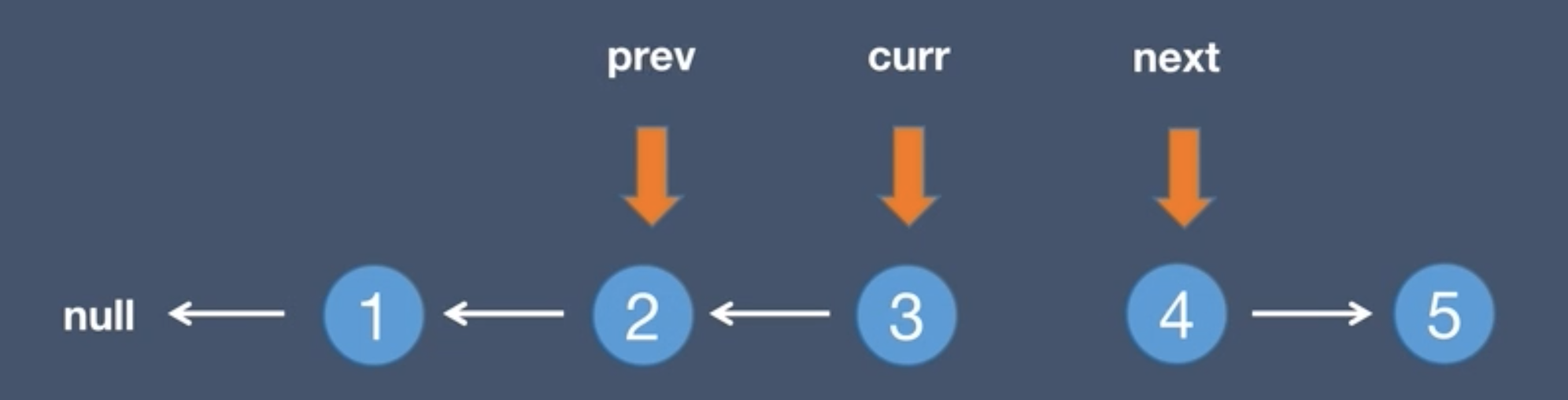
7.Loop traversal



Code
package LinkedLists;
/**
* @author zhengstars
* @date 2023/08/19
*/
public class ReverseLinkedList {
public static class ListNode {
int value;
ListNode next;
public ListNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
public static ListNode reverseLinkedList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode curr = head;
ListNode next = null;
while (curr != null) {
next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
}
Reverse Linked List II
Solution (Iterate and insert the following node of curr to the position after pre)
- Save the next node of the current node,
ListNode next = curr.next - Let the next pointer of the current node point to the node pointed by next’s next pointer.
curr.next = next.next; - Point the next of the
nextnode to the node pointed by pre’s next pointer .next.next = pre.next - Move the
nextpointer to the position after the pre pointer, by setting thenextpointer of the pre poniter to thenextpointer.pre.next = next;
Step
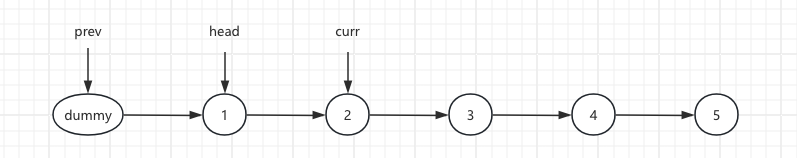
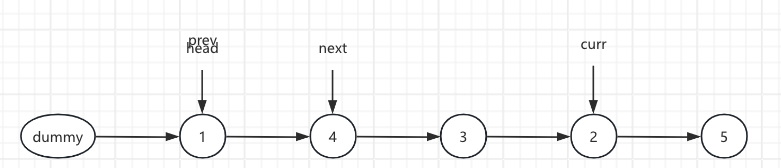
1.Initial List and Pre(head) Node
left = 2, right = 4. After the pre loop, pre points to 1 and curr points to 2.
2.Initial List and Next Node, next = curr.next
Before: curr.next = 3
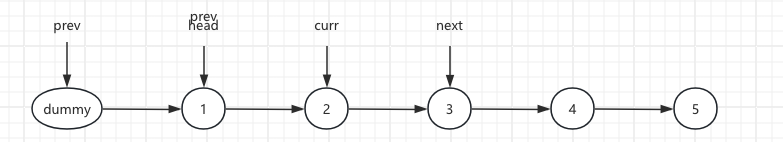
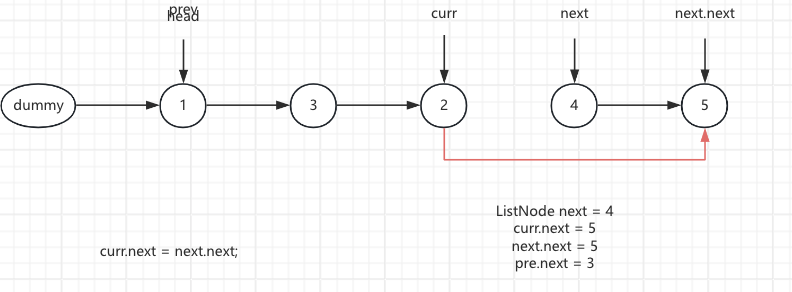
3.The current.next points to the pre.next node, curr.next = next.next
After: curr.next = 4
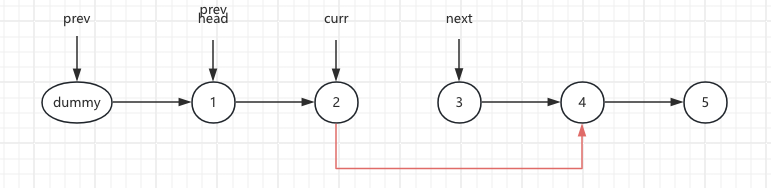
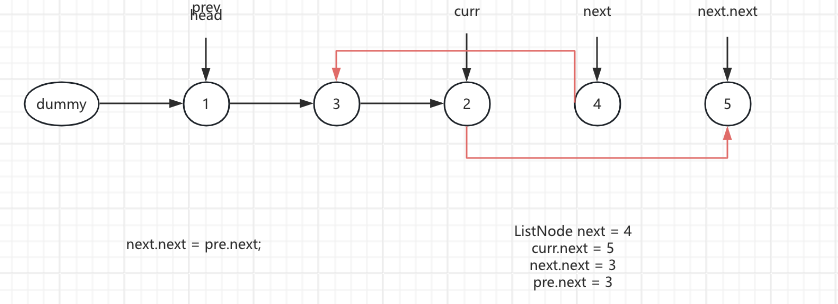
4.The next.next node points to the pre.next. next.next = pre.next
next.next = pre.next; curr.next = 4 next.next = 2 pre.next = 2
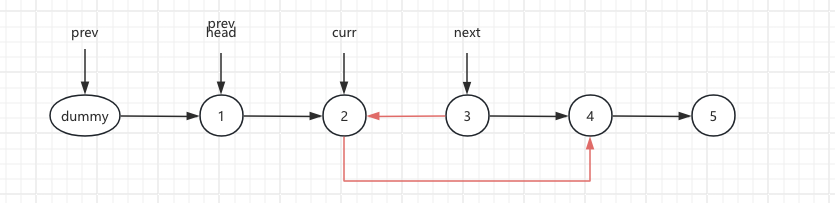
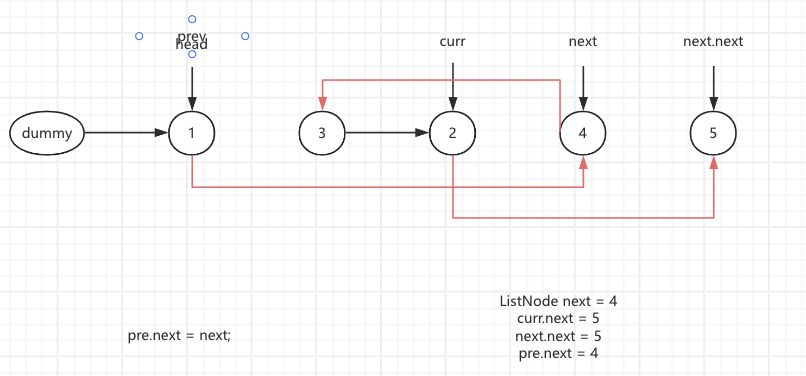
5.The pre node points to the next node, pre.next = next
curr.next = 4 next.next = 2 pre.next = 3
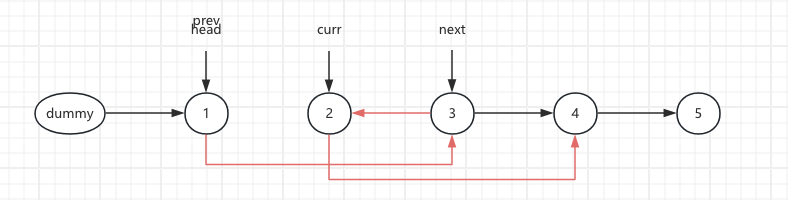
6.Loop1
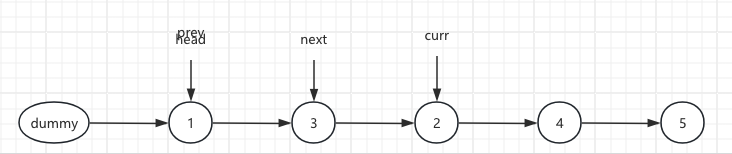
7.Repeat step 2 to 5 , loop traversal, until to meet the end of range
ListNode next = 4 curr.next = 4 next.next = 5 pre.next = 3
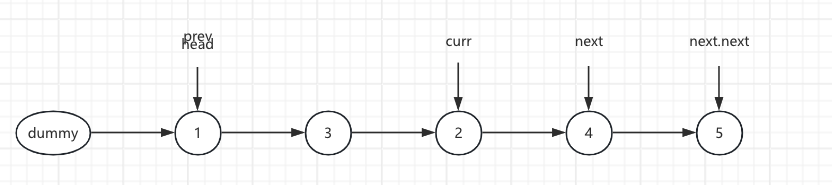
8.Loop traversal
Code
package LinkedLists;
/**
* @author zhengstars
* @date 2025/09/21
*/
public class ReverseLinkedListII {
public static class ListNode {
int value;
ListNode next;
public ListNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
public static ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) {
if (head == null || left == right) {
return head;
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummy;
for (int i = 1; i < left; i++) {
pre = pre.next;
}
ListNode curr = pre.next;
for (int i = 0; i < right - left; i++) {
ListNode next = curr.next;
curr.next = next.next;
next.next = pre.next;
pre.next = next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: